-
[Forex] VocabularyForex 2021. 10. 4. 23:35
Forex (Foreign Exchange)
- it’s the global financial market that allows one to trade currencies.
Liquidity
- Liquidity is used to describe the level of activity in the financial market.
In forex, it’s based on the number of active traders buying and selling a specific currency pair and the volume being traded.
The more frequently traded something is the higher its liquidity.
For example, more people trade the EUR/USD currency pair and at higher volumes than the AUD/USD currency pair.
This means that EUR/USD is more liquid than AUD/USD.
Spot FX
- The spot FX market is an “off-exchange” market, also known as an over-the-counter (“OTC”) market.
- In an OTC market, a customer trades directly with a counterparty.
- It’s important to point out that you are NOT trading the underlying currencies themselves,
but a contract involving the underlying currencies.- For example, an institution buys EUR/USD in the spot FX market.
The trade opened and closed on Monday has a value date on Wednesday.
This means that it’ll receive euros on Wednesday.*T+2 : Today plus 2 business days
Retail Forex
*Forex trading providers trade in the primary OTC market on your behalf.
They find the best available prices and then add a “markup” before displaying the prices on their trading platforms.*Forex trading providers are also known as “forex brokers”
Trading exmaple
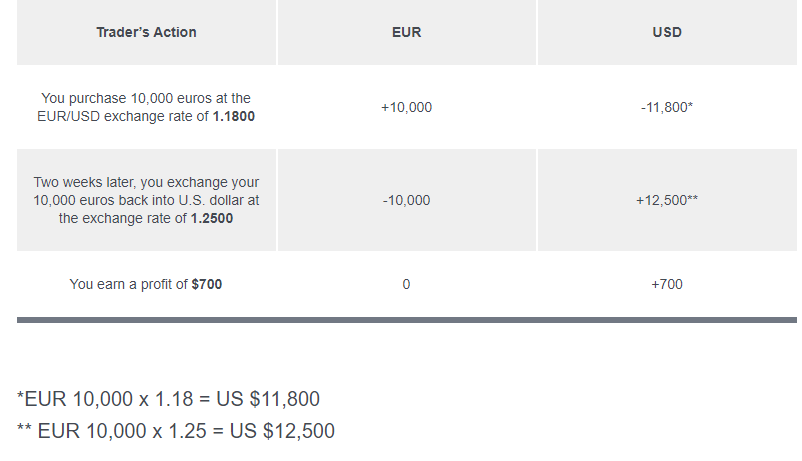
Symbol
GBP / USD = 1.21228
GBP : Base Currency
USD : Counter/Quote Currency“Long” and “Short”
long = buy : buy the base currency and sell the quote currency
short = sell : sell the base currency and buy the quote currencyFlat or Square
f you have no open position, then you are said to be “flat” or “square”.
Closing a position is also called “squaring up“.
The Bid, Ask and Spread
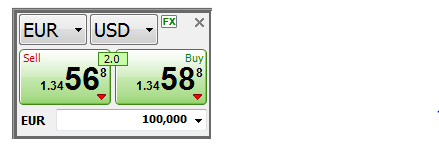
based on USER All forex quotes are quoted with two prices: the bid and ask.
In general, the bid(left) is lower than the ask(right) price.
When you buy a currency, you will use the offer or ASK price(right).
When you sell, you will use the BID price(left).
*Bid(Bid price, price in "sell" section(left one the above picture) )
The bid is the price at which your broker is willing to buy the base currency in exchange for the quote currency.
This means the bid is the best available price at which you (the trader) can sell to the market.
If you want to sell something, the broker will buy it from you at the bid price.
"broker Buy, and trader sell. "
"Sell 1.34568 means that Trader selling 1 EUR and Buying 1.34568 USD"*Ask( Ask price, price in "buy" section(right one the above picture))
he ask is the price at which your broker will sell the base currency in exchange for the quote currency.
This means the ask price is the best available price at which you can buy from the market.
Another word for ask is the offer price.
If you want to buy something, the broker will sell (or offer) it to you at the ask price
"Broker Sell, and trader Buy"
"buy 1.34588 means that Trader Buying 1 EUR at 1.34568 USD"*Spread
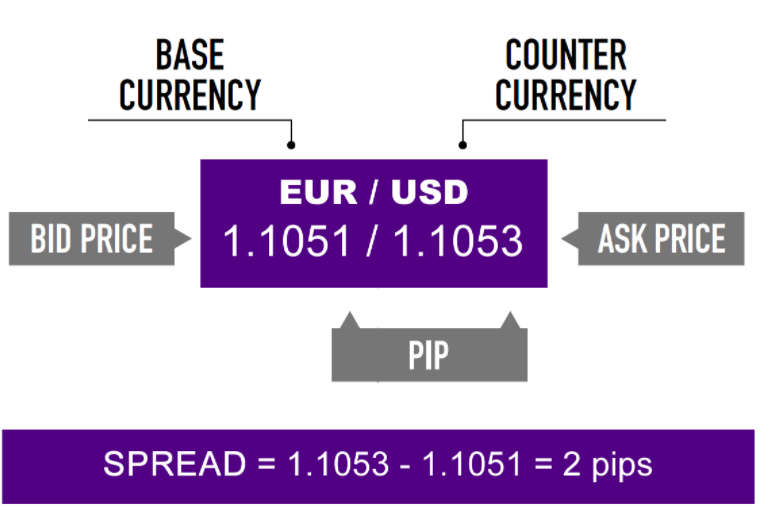
based on Broker Traders
- If you want to sell EUR, you click “Sell” and you will sell euros at 1.1051
- If you want to buy EUR, you click “Buy” and you will buy euros at 1.1053Brokers
- Buying 1 EUR at 1.1051
- Selling 1 EUR at 1.1053
- 20 points = 2 pipsLots
Standard Lot = 100,000 units
Mini lot = 10,000 units
Micro lot = 1000 units
Nano lot = 100 units
Margin
When you trade with leverage, you wouldn’t need to pay the 10,000 euros upfront.
Instead, you’d put down a small “deposit”, known as Margin- You believe that signals in the market are indicating that the British pound will go up against the U.S. dollar.
- You open one standard lot (100,000 units GBP/USD), buying with the British pound with a 2% margin requirement.
- You wait for the exchange rate to climb.
- When you buy one lot (100,000 units) of GBP/USD at a price of 1.50000, you are buying 100,000 pounds, which is worth $150,000 (100,000 units of GBP * 1.50000).
- Since the margin requirement was 2%, then US$3,000 would be set aside in your account to open up the trade ($150,000 * 2%).
- You now control 100,000 pounds with just $3,000.
- Your predictions come true and you decide to sell. You close the position at 1.50500. You earn about $500.
Leverage
Leverage is the ratio of the transaction size(=Position size) to the actual cash(=trading capital) used for margin
for example, 50:1 Leveage(= 2% margin requirement) means $2,000 of margin
is required to open a position size worth $100,000Assuming that this USD/JPY trade is the only position you have open in your account, you would have to maintain your account’s equity (absolute value of your trading account) of at least $1,000 at all times in order to be allowed to keep the trade open.
If USD/JPY plummets and your trading losses cause your account equity to fall below $1,000, the broker’s system would automatically close out your trade to prevent further losses.
Rollover
Rollover fee = swap feeevery currency trade involves borrowing one currency to buy another,
interest rollover charges are part of forex trading.If you are buying a currency with a higher interest rate than the one you are borrowing, then the net interest rate differential will be positive (i.e. USD/JPY) and you will earn interest as a result.
Conversely, if the interest rate differential is negative then you will have to pay.
per Pip Calculation
- USD/JPY at an exchange rate of 119.80: (.01 / 119.80) x 100,000 = $8.34 per pip
- USD/CHF at an exchange rate of 1.4555: (.0001 / 1.4555) x 100,000 = $6.87 per pip
Calculation profit and loss
- The rate you are quoted is 1.4525 / 1.4530. Because you are buying U.S. dollars you will be working on the “ASK” price of 1.4530, the rate at which traders are prepared to sell.
- So you buy 1 standard lot (100,000 units) at 1.4530.
- A few hours later, the price moves to 1.4550 and you decide to close your trade.
- The new quote for USD/CHF is 1.4550 / 1.4555. Since you initially bought to open the trade, to close the trade, you now must sell in order to close the trade so you must take the “BID” price of 1.4550. The price that traders are prepared to buy at.
- The difference between 1.4530 and 1.4550 is .0020 or 20 pips.
- Using our formula from before, we now have (.0001/1.4550) x 100,000 = $6.87 per pip x 20 pips = $137.40
Order Type

Market Order
A market order is an order to buy or sell at the best available price.
You would click buy and your trading platform would instantly execute a buy order at that (hopefully) exact price.
Limit Order
A limit order is an order placed to either buy below the market or sell above the market at a certain price.
For example, EUR/USD is currently trading at 1.2050. You want to go short if the price reaches 1.2070.
If the price goes up to 1.2070, your trading platform will automatically execute a sell order at the best available price.
A limit order to BUY at a price below the current market price will be executed at a price equal to or less than the specified price.
A limit order to SELL at a price above the current market price will be executed at a price equal to or more than the specific price.
Stop Entry Order
A stop order “stops” an order from executing until price reaches a stop price.
You place a “Buy Stop” order to buy at a price above the market price, and it is triggered when the market price touches or goes through the Buy Stop price
You place a “Sell Stop” order to sell when a specified price is reached
Stop Loss Order
If you are in a long position, it is a sell STOP order.
If you are in a short position, it is a buy STOP order
For example, you went long (buy) EUR/USD at 1.2230. To limit your maximum loss, you set a stop loss order at 1.2200.
This means if you were dead wrong and EUR/USD drops to 1.2200 instead of moving up, your trading platform would automatically execute a sell order at 1.2200 the best available price and close out your position for a 30-pip loss (eww!).
Trailing Stop
Let’s say that you’ve decided to short USD/JPY at 90.80, with a trailing stop of 20 pips.
This means that originally, your stop loss is at 91.00. If the price goes down and hits 90.60, your trailing stop would move down to 90.80 (or breakeven).

Good ‘Till Cancelled (GTC)
A GTC order remains active in the market until you decide to cancel it. Your broker will not cancel the order at any time. Therefore, it is your responsibility to remember that you have the order scheduled
Good for the Day (GFD)
A GFD order remains active in the market until the end of the trading day.
One-Cancels-the-Other (OCO)
An OCO order is a combination of two entry and/or stop loss orders.
Let’s say the price of EUR/USD is 1.2040. You want to either buy at 1.2095 over the resistance level in anticipation of a breakout or initiate a selling position if the price falls below 1.1985.
The understanding is that if 1.2095 is reached, your buy order will be triggered and the 1.1985 sell order will be automatically canceled.
One-Triggers-the-Other (OTO)
An OTO is the opposite of the OCO, as it only puts on orders when the parent order is triggered.
forex 3-session system
These sessions consist of the Asian, European, and North American sessions,
which are also called Tokyo, London, and New York sessions.