-
[Nest.js] 14 - Log basicNest.js 2021. 9. 17. 12:02
Contents
1. Log?
2. Types of Logging
3. Log Level Example
4. logging Implementation
1. Log?
- When we run an application, we encount unexpected errors sometimes.
- Therefore, to see logs is a fast and useful way to find where an error occurs.
- It is a better way to put logs after every single implementation is done
- Nest.js provides Logger class, which is built-in.
2. Types Of Logging
- Log : A wide use of logging for an important infornmation
- Warning : unhandled issue which is NOT fatal or destructive
- Error : unhandled issue which is fatal or destructive
- Debug : when an error occurred, Debug logging is helpful to degub a login, intended for developers
- Verbose : provides an insight of information about application running, intended for operators
3. Log Level Example
LOG Error Warning Debug Verbose Development O O O O O Staging O O O X X Productuib O O X X X // this is one of logging level cases, so it might be different based on application environment.
4. logging Implementation
- src/main.ts
import { Logger, ValidationPipe } from '@nestjs/common'; ... async function bootstrap() { const logger = new Logger();// 1 const app = await NestFactory.create(AppModule); ... const port = 3000; await app.listen(port); logger.log(`Application running on port ${port}`); // 2 Logger.log(`Application running on port ${port}`); // 3 } bootstrap();// 1. create an instance of Logger class, which is nest.js built-in
// 2. use the method log(...), already implemented in its class
// 3. use the static method log(...), already implemented in its class,
- Check logs

- src/boards/boards.controller.ts
... import { ... Logger, } from '@nestjs/common'; @Controller('boards') @UseGuards(AuthGuard()) export class BoardsController { private logger = new Logger('JamesBoardsController'); // 1 constructor(private boardsService: BoardsService) {} ... @Get() getAllBoards(@GetUser() user: User): Promise<Board[]> { this.logger.log(`User ${user.username} trying to get all boards`); // 2 this.logger.error(`User ${user.username} trying to get all boards`); // 3 this.logger.warn(`User ${user.username} trying to get all boards`); // 4 this.logger.debug(`User ${user.username} trying to get all boards`); // 5 this.logger.verbose(`User ${user.username} trying to get all boards`); // 6 return this.boardsService.getAllBoards(user); } @Post() createBoard( @Body() createBoardDto: CreateBoardDto, @GetUser() user: User, ): Promise<Board> { this.logger.verbose( `User ${user.username} creating a new board. Payload : ${JSON.stringify(createBoardDto)}`, // 7 ); return this.boardsService.createBoard(createBoardDto, user); } ... }// 1. new Logger('JamesBoardsController') - label of the Logger class
// 2 ~ 6. see what differences are between those methods
// 7 ${ JSON.stringify(createBoardDto) - to make an object to JSON format
- Sign in the user "jamescha"
- Console logs for Read all boards with his token
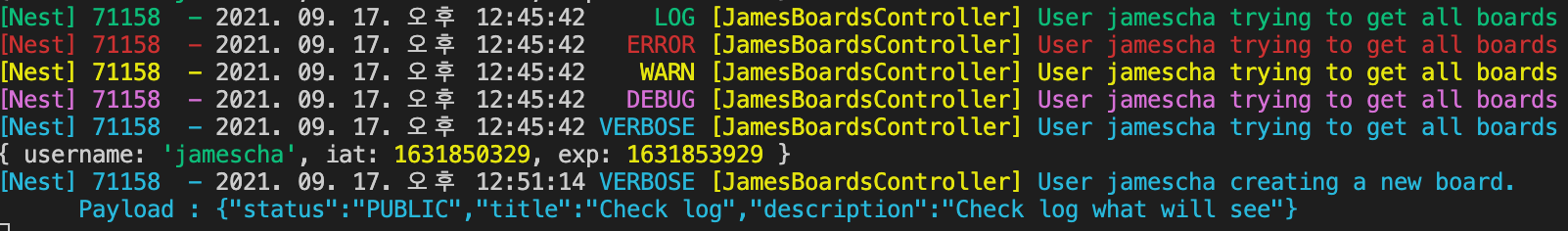
// Green - logger.log
// Red - logger.error
// Yellow - logger.warn
// Purple - logger.debug
// Blue - logger.verbose'Nest.js' 카테고리의 다른 글
[Nest.js] 16 - Log with Winston and WebHook (0) 2021.09.25 [Nest.js] 15 - Configuration (0) 2021.09.22 [Nest.js] 13 - Relations - One To One, Many To One (0) 2021.09.15 [Nest.js] 12 - Authentification - Passport & JWT (0) 2021.09.15 [Nest.js] 11 - Authentification - JWT (0) 2021.09.14