-
[Nest.js] simple projectNest.js 2021. 9. 27. 18:15
will cover very basics of Nest.js from creating a project to Building REST API.
Please make sure that we have installed
1. Node - v14.17.6
2. npm(Node Package Manager) - 7.20.3
3. Visual Studio Code
4. Postman (download link - https://www.postman.com/downloads/)
or Insomnia (download link - https://insomnia.rest/download)
STEP 1 - Install Nest.js
1.1 check node & npm version
$ node -v $ npm -v1.2 install nest.js using npm
$ npm i -g @nestjs/cli
STEP 2 - Build a basic project
2.1 create a nestjs project, and choose npm as package manager
$ nest new simple // "simple" is the project name2.2 open it in VSCode
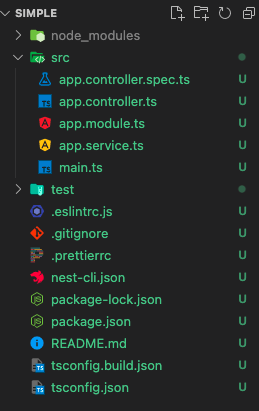
initial structure 2.3 run the application using npm
$ npm run start2.4 check it in a browser whether it runs OK
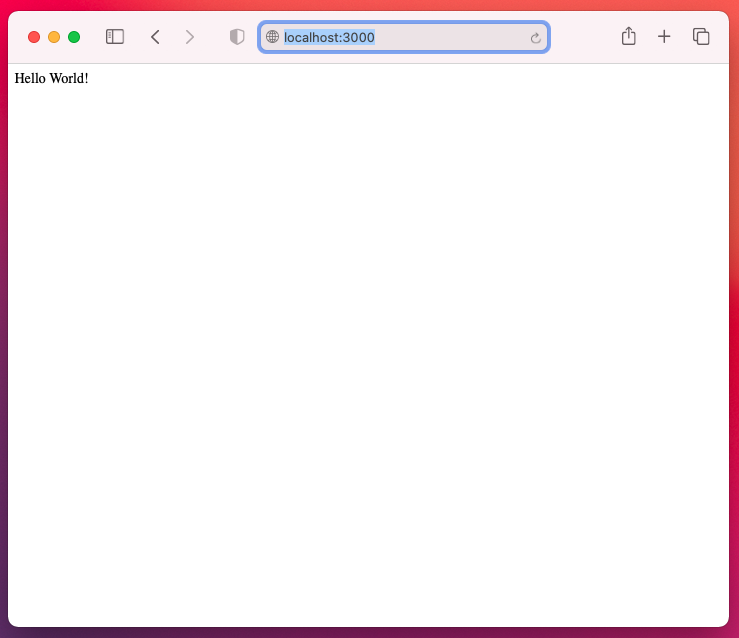
// if you see "Hello World!", it created properly.
2.5 let's remove some files that is not used in our simple project
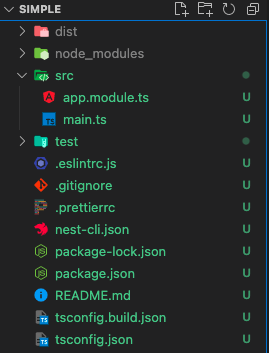
and, also remove those in app.module.ts
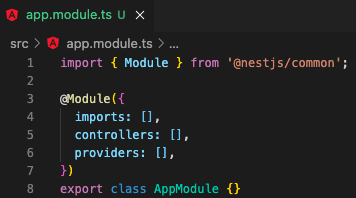
STEP3 - Module
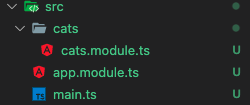
3.1 create a module, "cats"
$ nest g module cats// it is automatically registered in the Root module, "app.module.ts"
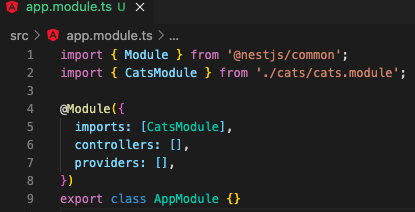
// also it created a folder, "cats", and "cats.module.ts" in its folder.
STEP4 - Controller & Service
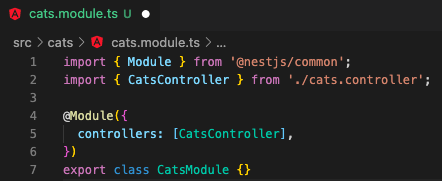
4.1 create a controller, "cats"
$ nest g controller cats // with testing file, preferred or $ nest g controller cats --no-spec // without testing file// it created in folder, "cats", and automatically registered in its module, "CatsModule".
4.2 create a service, "cats"
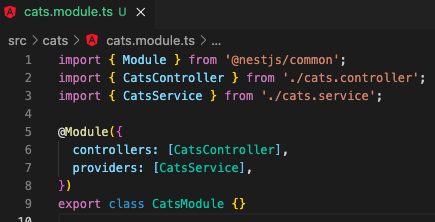
$ nest g service cats // with testing file, preferred or $ nest g service cats --no-spec // without testing file// it created in folder, "cats", and NOT registered in its module, "CatsModule".
4.3 register the service, "CatsService", into its module, "CatsModule"
4.4 create a folder, "dto", and a dto for request payload, "cat.dto.ts"
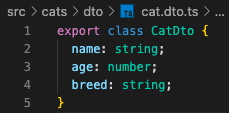
src/cats/dto/cat.dto.ts
STEP 5 - Implementation
5.1 implements "CatsService" first
import { Injectable } from '@nestjs/common'; import { CatDto } from './dto/cat.dto'; @Injectable() export class CatsService { private readonly cats: CatDto[] = []; // 1 create(catDto: CatDto) { // 2 this.cats.push(catDto); } findAll(): CatDto[] { // 3 return this.cats; } }// 1. use this as DB in this simple project
// 2. catDto: CatDto -> parameter name: Type
// 3. findall(): CatDto[] -> method name: Return Type
5.2 implement "CatsController"
import { Body, Controller, Get, Post } from '@nestjs/common'; import { CatsService } from './cats.service'; import { CatDto } from './dto/cat.dto'; @Controller('cats') // 1 export class CatsController { constructor(private catsService: CatsService) {} // 2 @Post() async create(@Body() catDto: CatDto) { // 3 this.catsService.create(catDto); } @Get() async findAll(): Promise<CatDto[]> { return this.catsService.findAll(); } }// 1. Route hadler entry point -> localhost:3000/cats
// 2. Dependency Injection
// 3. @Body() catDto: CatDto -> converts Request Payload into our CatDto
STEP 6 - Jest
6.1 module installation
$ npm i --save-dev @nestjs/testing6.2 Unit testing for the service, "cats.service.ts"
import { Test, TestingModule } from '@nestjs/testing'; import { CatsService } from './cats.service'; describe('CatsService', () => { // 1 let service: CatsService; beforeEach(async () => { const module: TestingModule = await Test.createTestingModule({ providers: [CatsService], }).compile(); service = module.get<CatsService>(CatsService); }); it('should be defined', () => { // 2 expect(service).toBeDefined(); }); describe('create', () => { // 1 it('should create a cat', () => { // 2 const beforeCreate = service.findAll().length; service.create({ name: 'test cat', age: 4, breed: 'unknown', }); const afterCreate = service.findAll().length; expect(afterCreate).toBeGreaterThan(beforeCreate); // 3 }); }); describe('finAll', () => { // 1 it('it should return an array', () => { // 2 const result = service.findAll(); expect(result).toBeInstanceOf(Array); // 3 }); }); });// 1. describe('XXX', () => {...}) : used for grouping several tests
1.1 first parameter : Name of the group showing in command line
1.2 second parameter : a callback function of the group// 2. it('XXX', () => {...}) : used for a test
2.1 first parameter : Name of a test
2.2 second parameter : test code implementation// 3. expect('XXX').METHOD('YYY') : making a result with developer's expectation
by comparing 'XXX' and 'YYY' with a METHOD6.3 run the above test file. (Testing files should have a .spec or .test suffix)
$ npm run test:cov // 1 or $ npm run test:watch // 2// 1. find test files and show a result of where and how much and tested as "%".
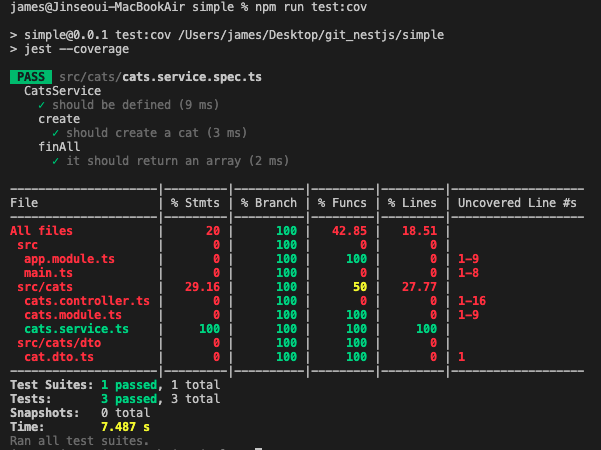
// % Stmts : represent instructions that have been executed at least once during the unit tests.
For example, we have a line that contains two statements: var age= 18; console.log(age)
this contains a variable declaration statement and a statement that executes the log function
that belongs to the console object.// % Branch : represent if statements which conditions have been fulfilled at least once during the unit tests
// % Funcs : represent functions that have been called at least once during the unit tests.
// % Lines : represent code lines that have executed at least once during the unit tests.
(added example of the % meanings)
6.4 e2e testing, preferred
- we have a e2e testing file as a defualt, in src/test/app.e2e-spec.ts
import { Test, TestingModule } from '@nestjs/testing'; import { INestApplication } from '@nestjs/common'; import * as request from 'supertest'; import { AppModule } from './../src/app.module'; describe('AppController (e2e)', () => { let app: INestApplication; beforeEach(async () => { const moduleFixture: TestingModule = await Test.createTestingModule({ imports: [AppModule], }).compile(); app = moduleFixture.createNestApplication(); await app.init(); }); describe('/cats', () => { it('/cats (GET)', () => { return request(app.getHttpServer()) // 1 .get('/cats') // 2 .expect(200) // 3 .expect([]); // 3 }); it('/cats (POST)', () => { return request(app.getHttpServer()) // 1 .post('/cats') // 2 .send({ // 4 name: 'TEST', age: 5, breed: "TEST cat" }) .expect(201); // 3 }); }); });// 1. creating a request
// 2. HttpMethod('url')
// 3. developer's expectation for the request
// 4. send a request payload to server.
6.5 run the e2e test file
$ npm run test:e2e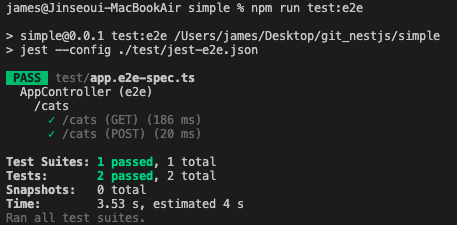
STEP 7 - API test
7.1 run the application
$ npm run start7.2 Using Postman or Insomnia, send a request that adding a cat
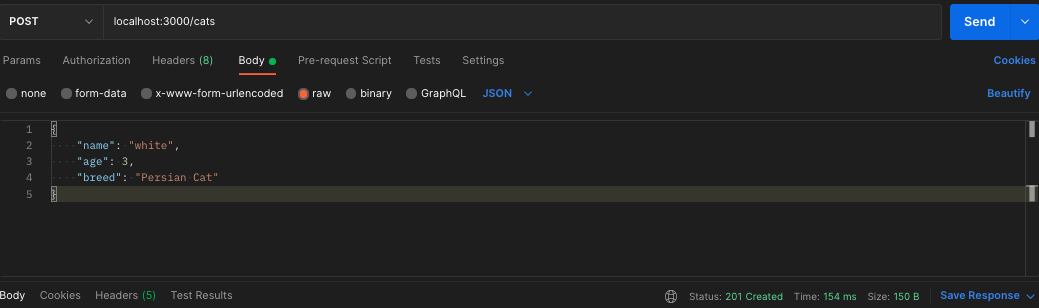
// Request url - localhost:3000/cats
// HTTP method - POST
// Request payload - Body -> raw -> JSON
// Result Status code - 201 created7.3 send a request that reading all cats
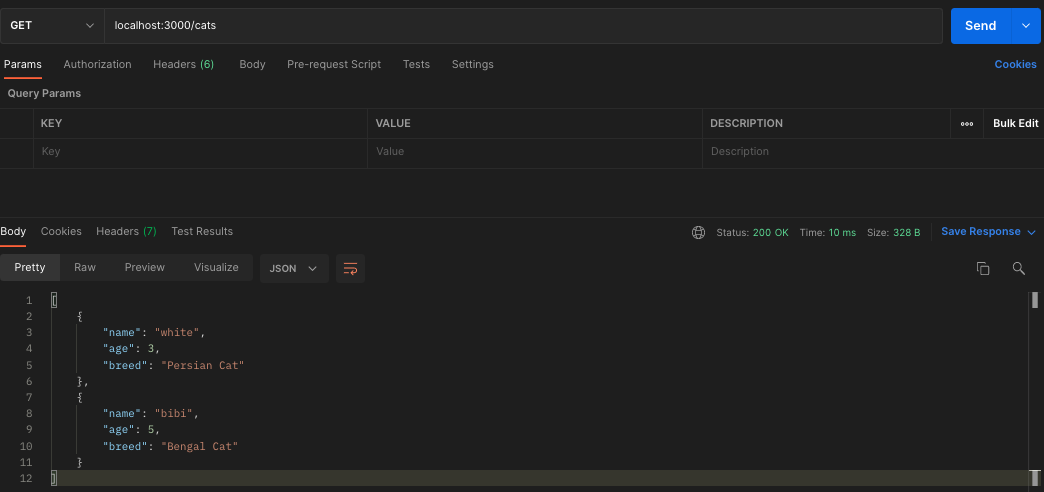
Additional STEP - Repository Pattern, TypeORM, MySQL
- There is the guildline of them, please follow the link
https://jinseo-copy-and-paste.tistory.com/11Thank you,
'Nest.js' 카테고리의 다른 글
[Nest.js] Life Cycle - 1 Middleware (0) 2021.10.01 [Nest.js] Life Cycle - advanced approach (0) 2021.09.29 [Nest.js] 16 - Log with Winston and WebHook (0) 2021.09.25 [Nest.js] 15 - Configuration (0) 2021.09.22 [Nest.js] 14 - Log basic (0) 2021.09.17